Is Stainless Steel Stronger Than Steel?
Stainless steel has become an increasingly popular material in various industries, including construction, transportation, and manufacturing, due to its corrosion-resistant properties and sleek appearance. However, there are still some misconceptions about the strength of stainless steel compared to traditional steel. Is stainless steel stronger than steel? This question has been a topic of debate in the engineering world for quite some time

- Huaxiao stainless steel suppliers in China
Is Stainless Steel Stronger Than Steel?
Yes, stainless steel is typically stronger than regular steel due to its higher levels of chromium and nickel. This also gives it increased resistance to corrosion and staining. However, the exact strength of stainless steel depends on the grade and specific composition used.
In this article, we will explore the differences between stainless steel and steel, their respective strengths, and how these materials are used in different applications. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of the strength of stainless steel and how it compares to steel. So, let’s dive into the details.ec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
TABLE OF CONTENT
key
difference between stainless steel and regular steel
difference
in properties between stainless steel and regular steel
difference
between stainless steel and other metals
difference
in application between stainless and regular steel
differences between stainless steel and regular steel
Stainless steel and regular steel, also known as carbon steel, are two different types of alloys that have unique properties and characteristics. The main difference between them lies in their composition and the way they are manufactured.
Composition
The difference in composition between stainless steel and regular steel lies in the type and content of alloying elements they contain.
Stainless steel is an alloy steel with high corrosion resistance and wear resistance, usually consisting of iron, chromium, nickel, and small amounts of carbon, manganese, and silicon. Among them, the content of chromium reaches more than 10.5%, which can form a dense oxide layer to protect the steel surface from corrosion. The nickel content contributes to the strength and plasticity of stainless steel and improves its corrosion and heat resistance.
When it comes to the composition of regular steel, it is mainly composed of carbon and iron. The carbon content of steel usually ranges from 0.2% to 2.1%, and the higher the carbon content, the harder the steel will be. In addition, the steel may contain other elements such as manganese, silicon, phosphorus, and sulfur to improve the mechanical properties of the steel. The content and proportions of these elements can be fine-tuned as needed to produce steels with specific properties.
In addition, stainless steel can also add other elements such as molybdenum, cobalt, titanium, etc., according to specific applications. These elements can further improve the corrosion resistance, strength and high temperature resistance of stainless steel and other characteristics. In short, the difference in composition between stainless steel and regular steel determines the differences in their physical properties, chemical properties, mechanical properties and uses.
Manufacturing

The differences in the manufacturing processes of stainless steel and regular steel are significant. Steel is produced by heating and melting ore in a blast furnace and mixing it with other materials (such as iron ore and coke). This process is known as basic steelmaking.
However, the manufacture of stainless steel requires the addition of other elements, such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. These elements improve the properties of stainless steel such as corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and strength. Stainless steel is generally manufactured by placing raw materials (e.g., steel, chromium, nickel, molybdenum, etc.) into an electric arc furnace, where they are heated to high temperatures and melted. By adjusting the type and proportion of added materials, different grades, and types of stainless steel can be obtained.
Regular Steel
Steelmaking
Steelmaking is the process of melting, reducing, and refining iron ore and other raw materials at high temperatures to obtain steel materials. This process usually takes place in a blast furnace or electric arc furnace and can vary depending on the raw material.
Continuous casting
The process of casting the refined steel into long bars or plates. This process can be divided into several steps such as billet casting, crystallizer, billet shell, and cooling.
Hot or Cold Rolling
The process of forming the billet at high or room temperature through several processes such as rolling and drawing. This process produces steel of different sizes, shapes, and surface finishes.
Surface treatment
The steel is surface treated through processes such as pickling, rust removal and spraying to make the steel surface flatter, smoother, rust-proof, etc.
processing
The steel is processed by shearing, cutting, stamping, drilling, welding, and other processing according to the need to adapt to different use scenarios and needs.
Stainless Steel
Smelting
Stainless steel is made by alloying iron, chromium, nickel, and other elements. In the smelting process, iron ore is first smelted into pig iron, and then pig iron and other alloying elements (such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum) are added to the furnace to make stainless steel through a high-temperature reaction and cooling process.
Rolling
Once smelting is complete, stainless steel is usually pressed into sheets or coils. These steels usually need to be rolled at high temperatures to change their shape and thickness. This process usually involves the use of a series of rolls and equipment to press the steel to the desired size and thickness.
Processing
The final step is to process the stainless steel into the desired shape, such as pipe, bar, plate, etc. Processing typically involves the use of a range of machining tools and equipment such as drill presses, punches, cutters and benders to cut, punch and bend the stainless steel material into the desired shape and size.
Overall, understanding the key differences between stainless steel and regular steel is crucial in selecting the appropriate material for your project. If you are in need of high-quality stainless steel, be sure to reach out to reputable stainless steel suppliers who can provide you with the best options for your specific needs.
differences in properties
The differences in composition between stainless steel and regular steel determine their physical properties, chemical properties, mechanical properties and uses.
corrosion resistance
Stainless steel has higher corrosion resistance compared to regular steel. This is determined by the chemical composition of stainless steel. Stainless steel contains at least 10.5% chromium, while ordinary steel has a higher iron content. Chromium forms a dense layer of chromium oxide in stainless steel, called a passivation layer, which prevents oxygen, water, and other corrosive substances from attacking the metal surface.
The passivation layer gives stainless steel excellent corrosion resistance to common forms of corrosion, such as water corrosion, oxidation corrosion, and acid corrosion. This allows stainless steel to maintain its appearance and performance stability in wet environments, chemical exposure, and high temperature conditions.
In addition, other alloying elements added to stainless steel, such as nickel, molybdenum and titanium, can further improve its corrosion resistance. These alloying elements enhance the oxidation resistance, acid resistance and alkaline resistance of stainless steel, making it suitable for more severe environments.
All in all, stainless steel has higher corrosion resistance than ordinary steel, which makes it the material of choice in many fields, including construction, chemicals, food processing, medical equipment, and marine engineering.
elasticity and ductility
Stainless steel has better elasticity and ductility compared to regular steel. This is due to the crystal structure and composition of stainless steel.
The crystal structure of stainless steel has a face-centered cubic (FCC) structure, which makes stainless steel has good elastic properties. It is able to recover its original shape after being stressed and is less likely to deform or break. This elasticity allows stainless steel to withstand high stresses and heavy loads in a variety of applications without losing its shape and structural integrity.
In addition, stainless steel has good ductility, also known as plasticity. It is able to undergo plastic deformation under stress without fracture. The high ductility of stainless steel allows it to be cold-worked and hot-worked into a variety of shapes such as plates, tubes, and bars to meet different needs.
This advantage of elasticity and ductility makes stainless steel widely used in many fields. For example, in building and structural engineering, stainless steel is able to withstand deformation and vibration without breaking and is therefore widely used in structural support for bridges, building frames, and high-rise buildings. In addition, in the automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and electronics fields, stainless steel is also an important material choice because of its superior elasticity and ductility.
Overall, stainless steel has better elasticity and ductility than ordinary steel, making it a reliable and versatile material for a variety of engineering and manufacturing applications.
heat resistance and wear resistance
First, stainless steel has good heat resistance in high-temperature environments. This is determined by the alloy composition and crystal structure of stainless steel. Among them, high-alloyed stainless steels (such as 316 and 310, etc.) have higher heat resistance and are able to maintain structural stability and strength at high temperatures. This makes stainless steel widely used in applications such as high-temperature processes, heat treatment, and combustion equipment.
Second, stainless steel also has better wear resistance. The wear resistance of stainless steel depends mainly on its hardness and surface finish. Alloying elements added to stainless steel, such as chromium, molybdenum and titanium, can improve its hardness and wear resistance. In addition, the wear resistance of stainless steel can be further enhanced by surface treatment methods such as polishing, sandblasting, and nitriding. This allows stainless steel to excel in applications where resistance to wear and corrosion is required, such as mechanical parts in manufacturing, food processing equipment, and chemical installations.
As a result, the high heat and wear resistance of stainless steel has led to its widespread use in many fields. Whether in high-temperature environments or where resistance to wear and tear is required, stainless steel provides long-lasting durability and reliable performance. This makes stainless steel an ideal material choice for a variety of engineering and manufacturing needs.
differences between stainless steel and other metal
Stainless steel exhibits excellent strength properties, making it a highly desirable material for various applications. When compared to other common metals, such as aluminum, copper, and carbon steel, stainless steel demonstrates notable strength characteristics.
The strength of stainless steel can vary depending on the specific grade and composition. It is typically stronger than aluminum and copper, which are known for their relatively lower strength levels. Stainless steel’s strength is often comparable to or slightly lower than that of carbon steel, a widely used construction material.
Stainless steel suppliers play a crucial role in providing different grades and forms of stainless steel with varying strength properties. They source stainless steel from manufacturers and ensure that the supplied material meets specific strength requirements. These suppliers collaborate with stainless steel producers to offer a wide range of options, allowing customers to select the appropriate grade with the desired strength for their intended applications.
Stainless steel’s strength is influenced by factors such as alloying elements, heat treatment, and manufacturing processes. By carefully controlling these variables, stainless steel suppliers can provide customers with stainless steel products that possess the required strength and mechanical properties.
In summary, stainless steel demonstrates competitive strength compared to other common metals. With the assistance of stainless steel suppliers, customers can access a diverse range of stainless steel grades, each with its own strength characteristics, enabling them to choose the most suitable material for their specific needs.
differences in application
building and construction industry


In the building and construction industry, stainless steel and regular steel play an important role, despite differences in their composition and properties. Regular steel is widely used as a load-bearing component of building structures such as beams, columns, and frames. Stainless steel, on the other hand, is widely used in building facades and exterior finishes, and its metallic luster and modern feel make it one of the materials of choice for designers. Stainless steel is also used in interior decoration, making staircase handrails, washbasins, kitchen countertops, etc. In addition, stainless steel plays an important role in architectural details and components, used in the manufacture of door and window fittings, connectors and bolts, etc. By partnering with stainless steel suppliers, construction and building companies can obtain the stainless steel materials needed to meet the requirements of various projects.
automotive and transportation manufacturing industries
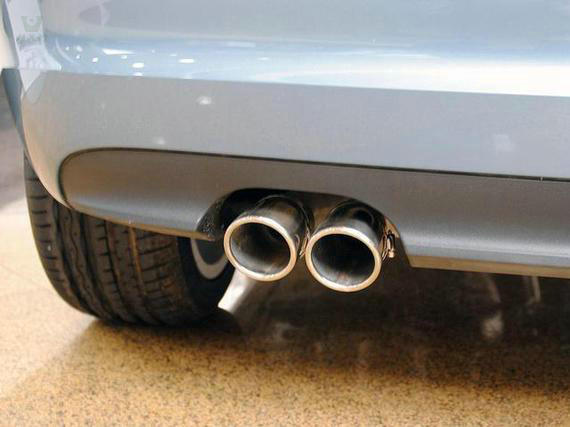
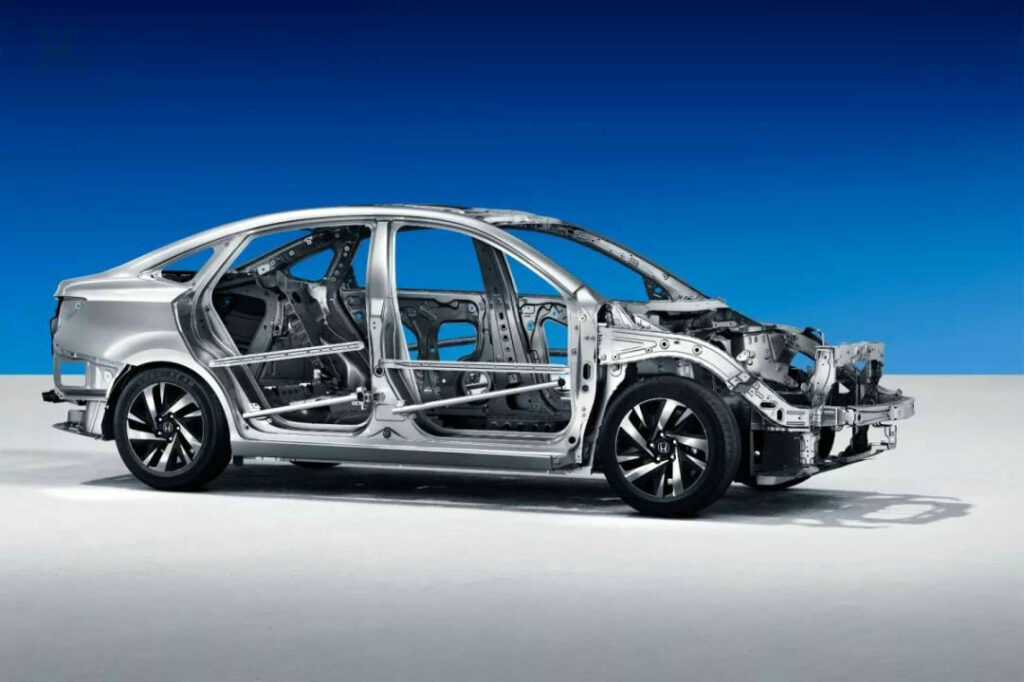


Both stainless and regular steels play an important role in the automotive and transportation manufacturing industries, although they differ in composition and performance. Regular steels are typically used in the body and chassis structure of automobiles to provide strong structural support and crash protection. Stainless steel, on the other hand, is increasingly used in automotive manufacturing. Stainless steel is corrosion and weather resistant and is therefore widely used in components such as automotive exterior trim, exhaust systems and emission controls. In addition, stainless steel is used to manufacture critical components such as brake systems, intake manifolds, fuel tanks and radiators to provide durability and reliability. By partnering with stainless steel suppliers, automotive and transportation manufacturers have access to high-quality stainless steel materials to meet the needs of a variety of applications and ensure product performance and reliability.
manufacturing industry


Both stainless steel and regular steel are widely used materials in the manufacturing industry, but there are some differences in their properties and uses. Regular steel is typically used to manufacture large structures and important mechanical components such as bridges, building structures, ships, and machinery. Regular steels have excellent strength and rigidity and can withstand high pressures and heavy loads. Stainless steel, on the other hand, also has an important place in manufacturing. Stainless steel has corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance, so it is widely used in the manufacture of chemical equipment, food processing equipment, medical equipment and aerospace components and other areas that require high levels of material purity and corrosion resistance. In addition, stainless steel is also used in the manufacturing industry to make automotive parts, electronic equipment housings, and household appliances. By working with stainless steel suppliers, manufacturers can obtain high-quality stainless steel materials and ensure the quality and performance of their products.
energy and petrochemical industries
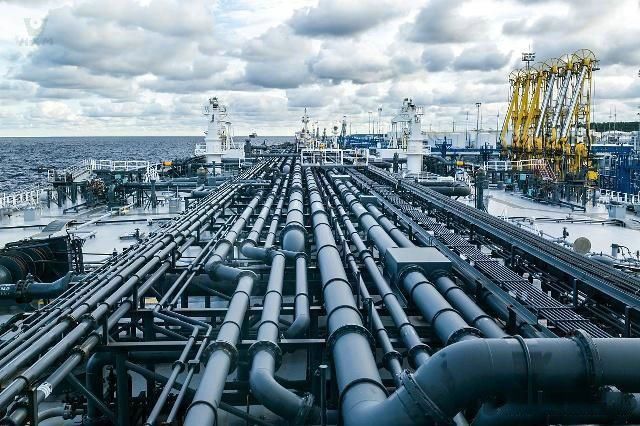


In the energy industry, stainless steel are often used in a variety of equipment and pipelines in the exploration, extraction, and transmission of oil and gas. In the petrochemical industry, stainless steel is widely used in the manufacture of chemical equipment, vessels, and pipelines.
Regular steels also have important applications in the energy and petrochemical industries. They are often used in construction, structural support, and the manufacture of large equipment, such as steel tanks and pressure vessels. Conventional steels typically have high strength and rigidity and are suitable for carrying loads of large structures and equipment.
By working with stainless steel suppliers, the energy and oil industries have access to high-quality stainless and regular steel materials.
Conclusion
In this article, we explore in detail the differences between stainless steel and regular steel and their applications in various industries. Although there are differences in composition, manufacturing processes, and properties between stainless steel and plain steel, they both play an important role in their respective fields.
In terms of strength, stainless steel can be less strong compared to plain steel, but still strong enough to meet the needs of many applications. Stainless steels offer significant advantages in terms of corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, heat resistance, and wear resistance, allowing them to perform at a higher level in specific environments.
It is important for consumers, manufacturers and stainless steel suppliers to understand the differences between stainless steel and regular steel. By choosing the right material, we can ensure that the product has the required performance and quality and meets the requirements of the specific industry.
So while stainless steel may not be as strong as regular steel in some areas, it is still a reliable and versatile choice for specific applications. Understanding the properties and applications of the material is key to making informed choices and decisions, whether as consumers, manufacturers or stainless steel suppliers, we can all take full advantage of stainless steel and be successful in our respective fields.

Duplex Steel 2205 Coils: Understanding the Applications and Uses
Duplex Steel 2205 Coils: Understanding the Applications and Uses Duplex Steel 2205 Coils Duplex Steel 2205 coils are widely used duplex stainless steel alloy known

What Are Steel Coils Used For ?
What are steel coils used for? stainless steel coils supplier in China Steel has been at the core of industrial development for centuries, and steel coils play
Top 10 Applications of Perforated Metal in Architectural Projects
Top 10 Applications of Perforated Metal in Architectural Projects perforated metal (stainless steel sheet) Perforated metal has long been a staple in industrial design, but

Guide to Stainless Steel Pipe Rolling: Process, Benefits, and Applications
Guide to Stainless Steel Pipe Rolling: Process, Benefits, and Applications stainless steel pipe What is Stainless steel pipe rolling? Stainless steel pipe rolling is a

How Are Stainless Steel Welded Tubes Made?
How Are Stainless Steel Welded Tubes Made? stainless steel welded tubes Stainless steel welded tubes are a vital component in various industries, including construction, automotive,

Comparing Stainless Steel Sheets: 409 vs. 410 vs. 410S vs. 420 vs. 430 vs. 440 vs. 446
Comparing Stainless Steel Sheets: 409 vs. 410 vs. 410S vs. 420 vs. 430 vs. 440 vs. 446 Each stainless steel sheet has its own unique



